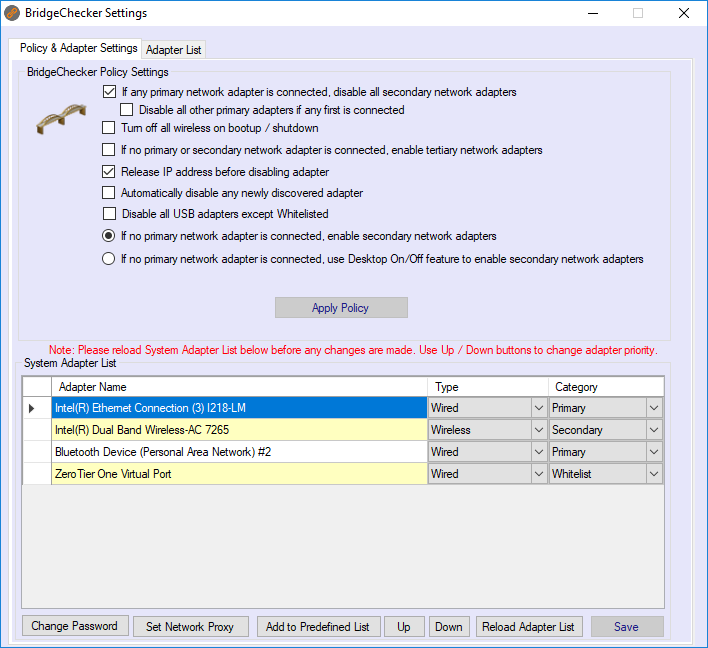
BridgeChecker for Windows is an easy-to-implement background application that can automatically disable/enable wireless interfaces for Windows devices on enterprise wireless networks. Powerful, useful, but simple. NEW FEATURE: Install parameter added for whitelisting specific adapters for Version 1.9.8 Build 705! A Blog About BridgeChecker for. BridgeChecker is a WiFi auto switch utility for Windows and Mac OS that can automatically disable/enable wireless interfaces. Whenever your computer is connected to an Ethernet port and the link state is good, the utility can automatically turn off the IEEE 802.11 wireless network interface. BridgeChecker is a File Transfer and Networking application like BWMeter, WinBox, and Ammyy Admin from AccessAgility, LLC. It has a simple and basic user interface, and most importantly, it is free to download.
- BridgeChecker is a Windows and Mac OS utility that can automatically dis. Disable Wireless When Connected to LAN Using BridgeChecker by AccessAgility®. BridgeChecker is a Windows and Mac OS.
- BridgeChecker Posted by Roger on 26 June 2009, 10:42 pm I’ve blogged several times about the desire to disable the wireless card when the wired card is connected.
This topic explains how to create a provisioning package using the Windows Configuration Designer, and apply it to Surface Hub devices. For Surface Hub, you can use provisioning packages to add certificates, install Universal Windows Platform (UWP) apps, and customize policies and settings.
You can apply a provisioning package using a USB stick during first-run setup, or through the Settings app.
Advantages
Quickly configure devices without using a mobile device management (MDM) provider.
No network connectivity required.
Simple to apply.
Requirements
To create and apply a provisioning package to a Surface Hub, you'll need the following:
- Windows Configuration Designer, which can be installed from Microsoft Store or from the Windows 10 Assessment and Deployment Kit (ADK). Learn how to install Windows Configuration Designer.
- A USB stick.
- If you apply the package using the Settings app, you'll need device admin credentials.

You create the provisioning package on a PC running Windows 10, save the package to a USB drive, and then deploy it to your Surface Hub.
Supported items for Surface Hub provisioning packages
Using the Provision Surface Hub devices wizard, you can:
- Enroll in Active Directory, Azure Active Directory, or MDM
- Create an device administrator account
- Add applications and certificates
- Configure proxy settings
- Add a Surface Hub configuration file
Warning
You must run Windows Configuration Designer on Windows 10 to configure Azure Active Directory enrollment using the wizard.
Using the advanced provisioning editor, you can add these items to provisioning packages for Surface Hub:
- Policies - Surface Hub supports a subset of the policies in the Policy configuration service provider.
- Settings - You can configure any setting in the SurfaceHub configuration service provider.
Tip
Use the wizard to create a package with the common settings, then switch to the advanced editor to add other settings.
Use the Surface Hub provisioning wizard
After you install Windows Configuration Designer, you can create a provisioning package.
Create the provisioning package
Bridgechecker Windows
Open Windows Configuration Designer:
From either the Start screen or Start menu search, type 'Windows Configuration Designer' and click on the Windows Configuration Designer shortcut,
or
If you installed Windows Configuration Designer from the ADK, navigate to
C:Program Files (x86)Windows Kits10Assessment and Deployment KitImaging and Configuration Designerx86(on an x64 computer) orC:Program FilesWindows Kits10Assessment and Deployment KitImaging and Configuration Designerx86ICD.exe(on an x86 computer), and then double-click ICD.exe.
Click Provision Surface Hub devices.
Name your project and click Next.
Configure settings
To provision the device with a certificate, click Add a certificate. Enter a name for the certificate, and then browse to and select the certificate to be used. |
Toggle Yes or No for proxy settings. The default configuration for Surface Hub is to automatically detect proxy settings, so you can select No if that is the setting that you want. However, if your infrastructure previously required using a proxy server and has changed to not require a proxy server, you can use a provisioning package to revert your Surface Hub devices to the default settings by selecting Yes and Automatically detect settings. If you toggle Yes, you can select to automatically detect proxy settings, or you can manually configure the settings by entering a URL to a setup script, or a static proxy server address. You can also identify whether to use the proxy server for local addresses, and enter exceptions (addresses that Surface Hub should connect to directly without using the proxy server). |
You can enroll the device in Active Directory and specify a security group to use the Settings app, enroll in Azure Active Directory to allow global admins to use the Settings app, or create a local administrator account on the device. To enroll the device in Active Directory, enter the credentials for a least-privileged user account to join the device to the domain, and specify the security group to have admin credentials on Surface Hub. If a provisioning package that enrolls a device in Active Directory is going to be applied to a Surface Hub that was reset, the same domain account can only be used if the account listed is a domain administrator or is the same account that set up the Surface Hub initially. Otherwise, a different domain account must be used in the provisioning package. Before you use a Windows Configuration Designer wizard to configure bulk Azure AD enrollment, set up Azure AD join in your organization. The maximum number of devices per user setting in your Azure AD tenant determines how many times the bulk token that you get in the wizard can be used. To enroll the device in Azure AD, select that option and enter a friendly name for the bulk token you will get using the wizard. Set an expiration date for the token (maximum is 30 days from the date you get the token). Click Get bulk token. In the Let's get you signed in window, enter an account that has permissions to join a device to Azure AD, and then the password. Click Accept to give Windows Configuration Designer the necessary permissions. To create a local administrator account, select that option and enter a user name and password. Important: If you create a local account in the provisioning package, you must change the password using the Settings app every 42 days. If the password is not changed during that period, the account might be locked out and unable to sign in. |
Toggle Yes or No for enrollment in MDM. If you toggle Yes, you must provide a service account and password or certificate thumbprint that is authorized to enroll the device, and also specify the authentication type. If required by your MDM provider, also enter the URLs for the discovery service, enrollment service, and policy service. Learn more about managing Surface Hub with MDM. |
You can install multiple Universal Windows Platform (UWP) apps in a provisioning package. For help with the settings, see Provision PCs with apps. Important: Although the wizard interface allows you to select a Classic Win32 app, only include UWP apps in a provisioning package that will be applied to Surface Hub. If you include a Classic Win32 app, provisioning will fail. |
You don't configure any settings in this step. It provides instructions for including a configuration file that contains a list of device accounts. The configuration file must not contain column headers. When you apply the provisioning package to Surface Hub, if a Surface Hub configuration file is included on the USB drive, you can select the account and friendly name for the device from the file. See Sample configuration file for an example. Important: The configuration file can only be applied during the out-of-box setup experience (OOBE) and can only be used with provisioning packages created using the Windows Configuration Designer released with Windows 10, version 1703. |
You can set a password to protect your provisioning package. You must enter this password when you apply the provisioning package to a device. |
After you're done, click Create. It only takes a few seconds. When the package is built, the location where the package is stored is displayed as a hyperlink at the bottom of the page.
Sample configuration file
A Surface Hub configuration file contains a list of device accounts that your device can use to connect to Exchange and Skype for Business. When you apply a provisioning package to Surface Hub, you can include a configuration file in the root directory of the USB flash drive, and then select the desired account to apply to that device. The configuration file can only be applied during the out-of-box setup experience (OOBE) and can only be used with provisioning packages created using the Windows Configuration Designer released with Windows 10, version 1703.
Use Microsoft Excel or other CSV editor to create a CSV file named SurfaceHubConfiguration.csv. In the file, enter a list of device accounts and friendly names in this format:
Important
Because the configuration file stores the device account passwords in plaintext, we recommend that you update the passwords after you've applied the provisioning package to your devices. You can use the DeviceAccount node in the Surface Hub configuration service provider (CSP) to update the passwords via MDM.
The following is an example of SurfaceHubConfiguration.csv.
Use advanced provisioning
Bridgechecker Free
After you install Windows Configuration Designer, you can create a provisioning package.
Create the provisioning package (advanced)
Open Windows Configuration Designer:
From either the Start screen or Start menu search, type 'Windows Configuration Designer' and click on the Windows Configuration Designer shortcut,
or
If you installed Windows Configuration Designer from the ADK, navigate to
C:Program Files (x86)Windows Kits10Assessment and Deployment KitImaging and Configuration Designerx86(on an x64 computer) orC:Program FilesWindows Kits10Assessment and Deployment KitImaging and Configuration Designerx86ICD.exe(on an x86 computer), and then double-click ICD.exe.
Click Advanced provisioning.
Name your project and click Next.
Select Common to Windows 10 Team, click Next, and then click Finish.
In the project, under Available customizations, select Common Team settings.
Add a certificate to your package
You can use provisioning packages to install certificates that will allow the device to authenticate to Microsoft Exchange.
Note
Provisioning packages can only install certificates to the device (local machine) store, and not to the user store. If your organization requires that certificates must be installed to the user store, use Mobile Device Management (MDM) to deploy these certificates. See your MDM solution documentation for details.
In the Available customizations pane, go to Runtime settings > Certificates > ClientCertificates.
Enter a CertificateName and then click Add.
Enter the CertificatePassword.
For CertificatePath, browse and select the certificate.
Set ExportCertificate to False.
For KeyLocation, select Software only.
Add a Universal Windows Platform (UWP) app to your package
Before adding a UWP app to a provisioning package, you need the app package (either an .appx, or .appxbundle) and any dependency files. If you acquired the app from the Microsoft Store for Business, you will also need the unencoded app license. See Distribute offline apps to learn how to download these items from the Microsoft Store for Business.
In the Available customizations pane, go to Runtime settings > UniversalAppInstall > DeviceContextApp.
Enter a PackageFamilyName for the app and then click Add. For consistency, use the app's package family name. If you acquired the app from the Microsoft Store for Business, you can find the package family name in the app license. Open the license file using a text editor, and use the value between the <PFM>...</PFM> tags.
For ApplicationFile, click Browse to find and select the target app (either an *.appx or *.appxbundle).
For DependencyAppxFiles, click Browse to find and add any dependencies for the app. For Surface Hub, you will only need the x64 versions of these dependencies.
If you acquired the app from the Microsoft Store for Business, you will also need to add the app license to your provisioning package.
Make a copy of the app license, and rename it to use a .ms-windows-store-license extension. For example, 'example.xml' becomes 'example.ms-windows-store-license'.
In ICD, in the Available customizations pane, go to Runtime settings > UniversalAppInstall > DeviceContextAppLicense.
Enter a LicenseProductId and then click Add. For consistency, use the app's license ID from the app license. Open the license file using a text editor. Then, in the <License> tag, use the value in the LicenseID attribute.
Select the new LicenseProductId node. For LicenseInstall, click Browse to find and select the license file that you renamed in Step 1.
Add a policy to your package
Surface Hub supports a subset of the policies in the Policy configuration service provider. Some of those policies can be configured with ICD.
In the Available customizations pane, go to Runtime settings > Policies.
Select one of the available policy areas.
Select and set the policy you want to add to your provisioning package.
Add Surface Hub settings to your package
You can add settings from the SurfaceHub configuration service provider to your provisioning package.
In the Available customizations pane, go to Runtime settings > SurfaceHub.
Select one of the available setting areas.
Select and set the setting you want to add to your provisioning package.
Build your package
When you are done configuring the provisioning package, on the File menu, click Save.
Read the warning that project files may contain sensitive information, and click OK.
Important
When you build a provisioning package, you may include sensitive information in the project files and in the provisioning package (.ppkg) file. Although you have the option to encrypt the .ppkg file, project files are not encrypted. You should store the project files in a secure location and delete the project files when they are no longer needed.
On the Export menu, click Provisioning package.
Change Owner to IT Admin, which will set the precedence of this provisioning package higher than provisioning packages applied to this device from other sources.
Set a value for Package Version, and then select Next.
Tip
You can make changes to existing packages and change the version number to update previously applied packages.
Optional: You can choose to encrypt the package and enable package signing.
Enable package encryption - If you select this option, an auto-generated password will be shown on the screen.
Enable package signing - If you select this option, you must select a valid certificate to use for signing the package. You can specify the certificate by clicking Browse... and choosing the certificate you want to use to sign the package.
Important
We recommend that you include a trusted provisioning certificate in your provisioning package. When the package is applied to a device, the certificate is added to the system store and any package signed with that certificate thereafter can be applied silently.
Click Next to specify the output location where you want the provisioning package to go once it's built. By default, Windows ICD uses the project folder as the output location.
Optionally, you can click Browse to change the default output location.
Click Next.
Click Build to start building the package. The project information is displayed in the build page and the progress bar indicates the build status.
If you need to cancel the build, click Cancel. This cancels the current build process, closes the wizard, and takes you back to the Customizations Page.
If your build fails, an error message will show up that includes a link to the project folder. You can scan the logs to determine what caused the error. Once you fix the issue, try building the package again.
If your build is successful, the name of the provisioning package, output directory, and project directory will be shown.
If you choose, you can build the provisioning package again and pick a different path for the output package. To do this, click Back to change the output package name and path, and then click Next to start another build.
If you are done, click Finish to close the wizard and go back to the Customizations Page.
Select the output location link to go to the location of the package. Copy the .ppkg to an empty USB flash drive.
Apply a provisioning package to Surface Hub
There are two options for deploying provisioning packages to a Surface Hub. During the first run wizard, you can apply a provisioning package that installs certificates, or after the first-run program is complete, you can apply a provisioning package that configures settings, apps, and certificates by using Settings.
Apply a provisioning package during first run
Important
During the first-run program, you can only use provisioning packages to install certificates. Use the Settings app to install apps and apply other settings.
When you turn on the Surface Hub for the first time, the first-run program will display the Hi there page. Make sure that the settings are properly configured before proceeding.
Insert the USB flash drive containing the .ppkg file into the Surface Hub. If the package is in the root directory of the drive, the first-run program will recognize it and ask if you want to set up the device. Select Set up.
The next screen asks you to select a provisioning source. Select Removable Media and tap Next.
Select the provisioning package (*.ppkg) that you want to apply, and tap Next. Note that you can only install one package during first run.
The first-run program will show you a summary of the changes that the provisioning package will apply. Select Yes, add it.
If a configuration file is included in the root directory of the USB flash drive, you will see Select a configuration. The first device account in the configuration file will be shown with a summary of the account information that will be applied to the Surface Hub.
In Select a configuration, select the device name to apply, and then click Next.
The settings from the provisioning package will be applied to the device and OOBE will be complete. After the device restarts, you can remove the USB flash drive.
Apply a package using Settings
Insert the USB flash drive containing the .ppkg file into the Surface Hub.
From the Surface Hub, start Settings and enter the admin credentials when prompted.
Navigate to Surface Hub > Device management. Under Provisioning packages, select Add or remove a provisioning package.
Select Add a package.
Choose your provisioning package and select Add. You may have to re-enter the admin credentials if prompted.
You'll see a summary of the changes that the provisioning package will apply. Select Yes, add it.
You can install additional apps on your Surface Hub to fit your team or organization's needs. There are different methods for installing apps depending on whether you are developing and testing an app, or deploying a released app. This topic describes methods for installing apps for either scenario.
A few things to know about apps on Surface Hub:
- Surface Hub only runs Universal Windows Platform (UWP) apps. Apps created using the Desktop App Converter will not run on Surface Hub.
- Apps must be targeted for the Universal device family or Windows Team device family.
- Surface Hub only supports offline-licensed apps from Microsoft Store for Business.
- By default, apps must be Store-signed to be installed. During testing and development, you can also choose to run developer-signed UWP apps by placing the device in developer mode.
- When submitting an app to the Microsoft Store, developers need to set Device family availability and Organizational licensing options to make sure an app will be available to run on Surface Hub.
- You need admin credentials to install apps on your Surface Hub. Since the device is designed to be used in communal spaces like meeting rooms, people can't access the Microsoft Store to download and install apps.
Develop and test apps
While you're developing your own app, there are a few options for testing apps on Surface Hub.
Developer Mode
By default, Surface Hub only runs UWP apps that have been published to and signed by the Microsoft Store. Apps submitted to the Microsoft Store go through security and compliance tests as part of the app certification process, so this helps safeguard your Surface Hub against malicious apps.
By enabling developer mode, you can also install developer-signed UWP apps.
Important
After developer mode has been enabled, you will need to reset the Surface Hub to disable it. Resetting the device removes all local user files and configurations and then reinstalls Windows.
To turn on developer mode
- From your Surface Hub, start Settings.
- Type the device admin credentials when prompted.
- Navigate to Update & security > For developers.
- Select Developer mode and accept the warning prompt.
Visual Studio
During development, the easiest way to test your app on a Surface Hub is using Visual Studio. Visual Studio's remote debugging feature helps you discover issues in your app before deploying it broadly. For more information, see Test Surface Hub apps using Visual Studio.
Provisioning package
Use Visual Studio to create an app package for your UWP app, signed using a test certificate. Then use Windows Imaging and Configuration Designer (ICD) to create a provisioning package containing the app package. For more information, see Create provisioning packages.
Submit apps to the Microsoft Store

Once an app is ready for release, developers need to submit and publish it to the Microsoft Store. For more information, see Publish Windows apps.
During app submission, developers need to set Device family availability and Organizational licensing options to make sure the app will be available to run on Surface Hub.
To set device family availability
On the Windows Dev Center, navigate to your app submission page.
Select Packages.
Under Device family availability, select these options:
- Windows 10 Team
- Let Microsoft decide whether to make the app available to any future device families
For more information, see Device family availability.
To set organizational licensing
On the Windows Dev Center, navigate to your app submission page.
Select Pricing and availability.
Under Organizational licensing, select Allow disconnected (offline) licensing for organizations.
Note
Make my app available to organizations with Store-managed (online) licensing and distribution is selected by default.
Note
Developers can also publish line-of-business apps directly to enterprises without making them broadly available in the Store. For more information, see Distribute LOB apps to enterprises.
For more information, see Organizational licensing options.
Deploy released apps
There are several options for installing apps that have been released to the Microsoft Store, depending on whether you want to evaluate them on a few devices, or deploy them broadly to your organization.
To install released apps:
- Download the app using the Microsoft Store app, or
- Download the app package from the Microsoft Store for Business, and distribute it using a provisioning package or a supported MDM provider.
Microsoft Store app
To evaluate apps released on the Microsoft Store, use the Microsoft Store app on the Surface Hub to browse and download apps.
Note
Using the Microsoft Store app is not the recommended method of deploying apps at scale to your organization:
- To download apps, you must sign in to the Microsoft Store app with a Microsoft account or organizational account. However, you can only connect an account to a maximum of 10 devices at once. If you have more than 10 Surface Hubs, you will need to create multiple accounts or remove devices from your account between app installations.
- To install apps, you will need to manually sign in to the Microsoft Store app on each Surface Hub you own.
To browse the Microsoft Store on Surface Hub
- From your Surface Hub, start Settings.
- Type the device admin credentials when prompted.
- Navigate to This device > Apps & features.
- Select Open Store.
Download app packages from Microsoft Store for Business
To download the app package you need to install apps on your Surface Hub, visit the Microsoft Store for Business. The Store for Business is where you can find, acquire, and manage apps for the Windows 10 devices in your organization, including Surface Hub.
Note
Currently, Surface Hub only supports offline-licensed apps available through the Store for Business. App developers set offline-license availability when they submit apps.
Find and acquire the app you want, then download:
- The offline-licensed app package (either an .appx or an .appxbundle)
- The unencoded license file (if you're using provisioning packages to install the app)
- The encoded license file (if you're using MDM to distribute the app)
- Any necessary dependency files
For more information, see Download an offline-licensed app.
Provisioning package
You can manually install the offline-licensed apps that you downloaded from the Store for Business on a few Surface Hubs using provisioning packages. Use Windows Imaging and Configuration Designer (ICD) to create a provisioning package containing the app package and unencoded license file that you downloaded from the Store for Business. For more information, see Create provisioning packages.
Supported MDM provider
To deploy apps to a large number of Surface Hubs in your organization, use a supported MDM provider. The table below shows which MDM providers support deploying offline-licensed app packages.
| MDM provider | Supports offline-licensed app packages |
|---|---|
| On-premises MDM with Configuration Manager (beginning in version 1602) | Yes |
| Third-party MDM provider | Check to make sure your MDM provider supports deploying offline-licensed app packages. |
To deploy apps remotely using Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager
Note
These instructions are based on the current branch of Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager.
Enroll your Surface Hubs into MDM management. For more information, see Manage Surface Hub with an MDM provider.
Download the offline-licensed app package, the encoded license file, and any necessary dependency files from the Store for Business. For more information, see Download an offline-licensed app. Place the downloaded files in the same folder on a network share.
In the Software Library workspace of the Configuration Manager console, click Overview > Application Management > Applications.
On the Home tab, in the Create group, click Create Application.
On the General page of the Create Application Wizard, select the Automatically detect information about this application from installation files check box.
In the Type drop-down list, select Windows app package (*.appx, *.appxbundle).
In the Location field, specify the UNC path in the form serversharefilename for the offline-licensed app package that you downloaded from the Store for Business. Alternatively, click Browse to browse to the app package.
On the Import Information page, review the information that was imported, and then click Next. If necessary, you can click Previous to go back and correct any errors.
On the General Information page, complete additional details about the app. Some of this information might already be populated if it was automatically obtained from the app package.
Click Next, review the application information on the Summary page, and then complete the Create Application Wizard.
Create a deployment type for the application. For more information, see Create deployment types for the application.
Deploy the application to your Surface Hubs. For more information, see Deploy applications with Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager.
As needed, update the app by downloading a new package from the Store for Business, and publishing an application revision in Configuration Manager. For more information, see Update and retire applications with Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager.
Note
If you are using Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager (current branch), you can bypass the above steps by connecting the Store for Business to Configuration Manager. By doing so, you can synchronize the list of apps you've purchased with Configuration Manager, view these in the Configuration Manager console, and deploy them like you would any other app. For more information, see Manage apps from the Microsoft Store for Business with Configuration Manager.
Bridgechecker
Summary
There are a few different ways to install apps on your Surface Hub depending on whether you are developing apps, evaluating apps on a small number of devices, or deploying apps broadly to your organization. This table summarizes the supported methods:
| Install method | Developing apps | Evaluating apps on a few devices | Deploying apps broadly to your organization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Studio | X | ||
| Provisioning package | X | X | |
| Microsoft Store app | X | ||
| Supported MDM provider | X |
Bridgechecker Free
More information
Bridgechecker Alternative
Related topics
